With the increase in infrastructure funding and construction projects to address growing environmental concerns, industry leaders are searching for materials that are both sustainable and cost-effective. Geosynthetic products, an increasingly popular category of advanced textiles, can fulfill this need for geotechnical civil engineering ventures. These materials can be used in soil stabilization, containment, reinforcement, filtering, and drainage while lowering construction costs, downtime, and long-term maintenance. With these upsides, the geosynthetics materials market is expected to climb to $13.2 billion by 2026.
Based on the size and scale of these projects, cutting and handling geosynthetics can pose a challenge. Industry leaders need equipment capable of managing the volume and variety of geosynthetic materials. Eastman offers a range of cutting and handling equipment for advanced textiles.
What Are Geosynthetics?
Geosynthetics is a broad term used to describe a range of petrochemical-based polymer planar products. They are highly durable against weather conditions and are biologically inert, meaning they cannot be damaged by bacteria or fungi.
Structures reinforced with geosynthetics do not require curing time like concrete alternatives, meaning they can be used right after construction is completed. Overall, the chemical makeup of geosynthetics contributes to a longer lifespan while lowering the need for and cost of maintenance.
Types of Geosynthetics
While there are several kinds of geosynthetics, the category can be loosely separated into geotextiles and geomembranes.
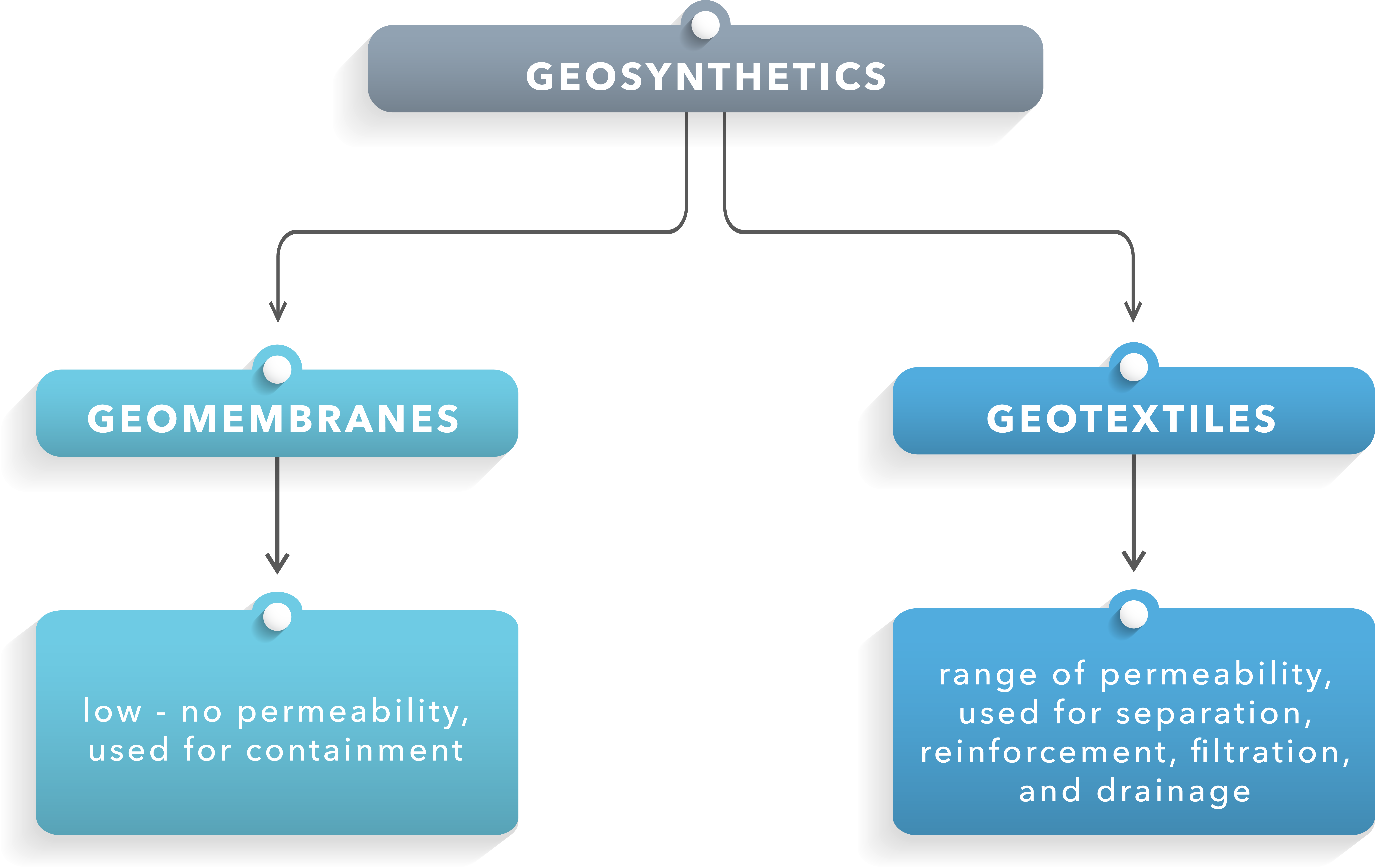
Geotextiles
Made of synthetic polymeric fibers, geotextiles are used for a range of terrain projects. Woven geotextile fabric features uniformly blended fibers that result in a high tensile strength, while non-woven geotextile fabrics are made up of random assorted fibers for high permeability. Woven geotextiles are suited for soil separation and reinforcement, while non-woven geotextiles are used for filtration and drainage.
Geomembranes
Geomembranes are thin continuous polymeric sheets used to contain various fluids or solid wastes. These layers, sometimes combined with asphalt, create a non-porous barrier to prevent hazardous infiltration.
How Are Geosynthetics Used?
Though geosynthetics have been in use for several decades, they are in increasingly high demand for modern-day erosion control, road construction, and landfill developments.
Erosion Control
Erosion is a global issue with environmental and economic repercussions. Geosynthetics can prevent erosion, limit leaching, and help recover soil fertility. Not only do they withstand rain contact, but they can also offer effective water filtration management while reinforcing seed and sediment placement.
Road Construction
With about one in 10 roads in the United States in poor condition and an influx of infrastructure spending, road construction is and will continue to be on the rise. Geosynthetics are already proven for use in reflective cracking mitigation in asphalt overlays, base stabilization, and subgrade stabilization.
Landfills
Like erosion, waste management poses significant problems worldwide. With high anti-seepage performance, tensile strength, and water and corrosion resistance, geomembranes in particular are installed to contain toxic and waste materials for the long term.
Cutting and Handling Solutions for Geosynthetic Materials
Industry leaders can turn to Eastman for all geosynthetic cutting and handling needs. Eastman equipment is industrial, reliable, and compatible with a full range of advanced textiles.
Manual Cutting
Many geosynthetics are cut onsite during the installation process due to the sheer size and scale of the materials. Eastman’s Hornet is a lightweight, convenient option for in-field cutting or any other area without outlet access. Cordless, handheld, and rechargeable, the Hornet delivers high torque at multiple speeds to easily cut through heavy-duty, industrial-grade textiles without any binding or tearing.
Automated Cutting
Eastman’s C135 Conveyor System uses proprietary InMotion™ software to continuously cut varying lengths of single- and low-ply rolled materials with precision and control. Computer-controlled, this machine requires minimal operator guidance to feed advanced textiles from the start position. Unique to customer material and application, the C135 has been configured as wide as 156 inches (3.96 meters).
Material Feeding & Handling
Take cutting room productivity to the next level with Eastman’s material handling equipment. Working with extremely heavy rolls of material? The Motor Driven Roll Stand has a 2,000-pound weight capacity and allows for conveyorized feeding with precision edge control. Controlled feeding speed is achieved through center-of-roll drive and an ultrasonic measuring beam. For cutting multi-ply of the same or different material, the Power Feed systems are available in one-roll, two-roll, three-roll, six-roll, and flat-fold configurations. The Power Feed simplifies material feeding to the cutting system by automatically adjusting and maintaining consistent tension.
See for Yourself
Live cutting demonstrations are available commitment-free, enabling customers and prospects to provide material and see the true output and performance of Eastman’s robust systems in person.

